Introduction
In web-fed printing, Cold Foil can be applied in Flexo-, Offset printing, and letterpress process.
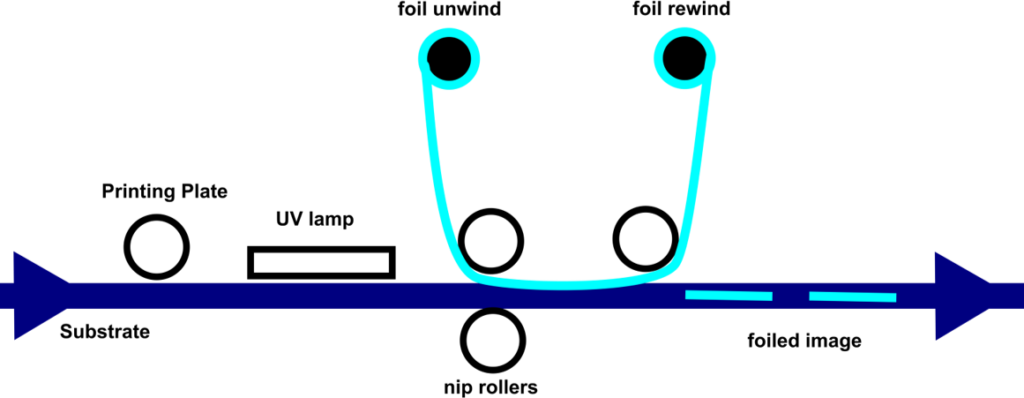
The majority of cold foil jobs are being produced in flexographic printing by using a UV-curing cold foil adhesive which is applied with an anilox roller in a specific volume via a polymer plate onto a substrate.
Immediately thereafter, the Cold Foil web is combined by means of a press roll with the substrate and adhesive. After this step, the UV adhesive is cured through the Cold Foil by UV radiation and the backing material is being removed. The metalized layer of cold foil remains on the areas which previously have been applied with adhesive. In the following printing units, the Cold Foil can be inline overprinted and many different multi-colored metallic effects can be achieved individually.
Depending on the absorbency of the used substrate, the adhesive amount must be amended to the right amount by the anilox roller volume and/or gravure if necessary.
The adhesive amount can be controlled very precisely over the used cell volume and the type of anilox roller in flexographic printing.
Benefits
- The transference of finest details, fonts, large areas, and screens is possible in a single run
- Inline- & Offline overprinting is possible
- No hot stamping clichés are necessary
- For the process no heat and no high pressure are required
- Application on heat-sensitive substrates possible
- The surface structure of the printing material is maintained on both sides
- Very short set-up and make-ready times and fast roll and job changes
- Very high production speeds
- Also optionally available as a shrink sleeve version for reverse effects
- Compared to metalized substrates no opaque white application is necessary, the white degree of the substrate can be optimally and efficiently used by avoiding the corresponding.
Markets / Typical uses
The Cold Foil finishing in web-fed printing is used for many different kinds of applications.
Diverse markets use a Cold Foil enhancement for their products to gain an added value.
For example the following ones:
- Food & Bevarage
- Cosmetics
- Personal care
- Pharmaceuticals
- Toys
- Electronic
- Non-Food
- Security
- Oil & Greases
- Lottery, Loyalty Programme and much more
Narrow-web printing machines for cold foiling
Foil finishing is becoming increasingly popular, in particular in the label sector. Cold foil applications are therefore also gaining importance in narrow web printing. Most self-adhesive label printing machines with a laminating station or rotary stamping unit will be suitable or can be adapted to this process. Most machine manufacturers also offer specially designed cold foil transfer units. Machine systems for cold foiling are now available from almost all printing machine manufacturers, for example:
- Aquaflex
- Codimag
- FOCUS
- Gallus
- Mark Andy
- MPS
- Nilpeter
- OMET
- Rotatek and others
The foil is usually supplied on 3-inch cores for these cold foiling modules.
The standard lengths are 2000 m – 4000 m, depending on the length of the substrate. The width should be approx. 0.5 cm wider than the desired design.
Machine capacities
The cold foiling modules differ with regard to their individual design features, for example, they may have a different web guiding system or method of regulating the foil tension or release. There is hardly any difference between them in terms of capacity, however. Depending on the substrate, design, and foil grade, processing speeds of 35 to 120 meters or more per minute are possible!
Printing processes
Cold foiling can be performed in conjunction with UV flexographic, UV offset, or UV letterpress printing. The most frequently used process in narrow web printing is flexographic printing. The processor can generally select freely between these options when choosing the process for applying cold foil. This is especially true given the current trend towards producing printing machines that are suitably equipped to perform the various printing methods on one and the same machine.
Printing Substrates for Cold Foil Transfer in Narrow-web Printing
Aside of paper and cardboard, the cold foil technology also offers the option to provide heat-sensitive materials with a partial metallic appearance.
Plastic materials such as PE, PP, PET
All commonly used plastic materials for self-adhesive labels, and even flexible packaging can be decorated. As with normal printing of UV inks on polyolefins (PE/PP), a corona pretreatment of the substrate should also be performed prior to cold foiling.
Papers with non-absorbent surfaces
Cold foil can without any difficulty well be applied to smooth, coated paper or cardboard.
In the case of very absorbent materials, however, the adhesive can penetrate into the substrate too quickly, so it is advisable to seal rough material surfaces by pre-printing a primer.
Special Application Inmold Labelling (IML)
Cold foil can also be transferred to stable plastic containers indirectly: by in-mold labeling. The motif is transferred to an IML substrate, then labels are punched out from the IMLreel and fixated in the injection molding die and the plastic material is injected from behind. The label is thereby firmly bonded to the substrate. Decorations by in-mold labeling may frequently be found on plastic containers for ice cream, margarine, ready-to-eat salads, or wall paint.
Why use cold foiling in narrow web printing?
Cold foiling in narrow web printing is an especially fast and flexible finishing technology.
It offers a high level of flexibility when creating the designs, and is also suitable for small print runs.
The process is therefore especially attractive for achieving the product varieties, trendy product variations and increasingly popular special packaging expected these days.
Cold foiling is also well suited for finishing mass produced products. Cold foil decoration is an extremely economical option.
Economic advantages
Low upfront costs No stamping dies are required, only conventional printing plates.
Rapid job changeovers
Machine setting and make-ready times are eliminated. Setup times are therefore very low. Color and design changeovers can be achieved as quickly as with straight printing projects.
Fast decoration process
As a rule, foil transfer occurs inline at close to conventional printing speeds. The speed of rotary narrow-web printing can therefore be utilized to full advantage for cold foiling. Speeds of up to 120m/min can be achieved.
Tangible benefits in label finishing
User defined coverage Metallized paper always has a full-surface coating.
With cold foiling, on the other hand, user defined areas can be covered with foil while at the same time leaving desired areas white.
The time-consuming step of preprinting with white, for example in the case of barcode fields, becomes unnecessary. Being able to optional blank out the foil also allows lighter colors to be printed clearly and without compromise.
Deformation-free transfer
No tensioning of the paper occurs when transferring cold foils, even for large-area designs. This allows the labels to be subsequently applied more quickly
Configuration of narrow-web printing machines
Here’s how to ensure problem-free foil transfer:
Coordinated processes
- The nip roller unit should immediately follow the printing of the UV adhesive; the nip roller should be manually or pneumatically adjustable.
- The web material should be guided in such a way that the printed side cannot come into contact with the face rollers as these could injure the not yet cured adhesive.
- The UV lamp should immediately follow the nip roller unit. Locating a counter-pressure roller under the UV lamp improves the contact between the foil and the material thereby facilitating curing.
- Foil release should occur immediately after the UV lamp and at the flattest angle possible so that the carrier foil layer of the cold foil releases well from the transferred design.
Clean transfer
The cold foil web must be absolutely wrinkle-free when fed to the nip roller otherwise perfect transfer will not be possible. The same applies to the subsequent transport of the substrate web, with the applied cold foil, to the UV lamp. The transfer results can also be negatively impacted by any contamination or entrapped air between the cold foil and the material web, or even dust on the material web.
Suitable lamp systems
All commonly available UV lamp systems with an output greater than 180 W/cm (the required lamp output depends on the actual printing speed) are suitable for curing the adhesive. Conventional high-pressure mercury UV lamps provide very good results.
Required quantity of adhesive
The criteria for determining the required quantity of UV adhesive are the material properties (smooth, absorbent) and the design of the cold foiling. Less adhesive is required for fine lettering or lines than for large areas; porous or matt materials also require larger quantities of adhesive than smooth, non-absorbent plastics. Based on experience, the required quantity of applied adhesive can vary between 3 and 10 g/m2 depending on the material properties.
The processing instructions provided by adhesive manufacturers should always be followed. The same applies to their recommendations regarding the use of additives like antifoaming agents, adhesion promoters, or photoinitiators.
Cold foils that can be used
Only cold foils specifically developed for this process will deliver a perfect transfer result. Some cold foils with particular color tones and effects cannot be used with this process due to their insufficient transparency to UV light.
Application hints
Printing of the UV adhesive:
- Use the correct flexographic printing plate; the hardness value should range between 65 and 70° Shore A
- Use a suitable adhesive tape to fasten the flexographic printing plate to the printing cylinder
- Use the correct UV adhesive – see the sections previous
- Use a suitable anilox roller with an appropriate volume; the correct coating weight depends on both the substrate and the design.High coating weight: 120 lines /cm ( approx. 300 lines / inch, 8 cm³/m² = 5.2 BCM) Medium coating weight: 180 lines / cm ( approx. 440 lines / inch, 6 cm³/m² = 3.9 BCM) Low coating weight: 220 lines / cm (approx. 550 lines / inch, 4.5 cm³/m² =2.6 BCM)
Laminating the cold foil onto the UV adhesive:
The hardness of the nip rollers is very important and should be around 90° Shore A.
UV curing
The distance between the laminating station and the UV curing unit should be no greater than 1 m. If the distance is greater, premature release, wrinkle, or bubble formation can occur, which will negatively impact the transfer.
Separation of the cold foil carrier
The release angle should be adjustable. Depending on the material, this release angle can be anywhere between very shallow and very high.
Things to be considered when using cold foils:
- The foil tension must be controlled – a too high tension can lead to wrinkles in the lengthwise direction, a too low tension can result in poor guiding of the foil.
- The speed of cold foil transfer is important. A too low speed can sometimes result in poorer transfer; a too high speed can result in inadequate curing of the UV adhesive.
- Selecting the design: It is necessary to ensure that the cold foil is in register with the substrate web. There is no means of saving foil. Labels with a border achieve the best utilization of the foil.
- Selecting the correct substrate: Not all available materials are suitable for use with cold foils. To date, it has not been possible to use structured, rough, or highly absorbent materials. Smooth, less absorbent, or plastic materials should therefore generally be selected.
About the Author:
Mohammed Abdul Haleem
Email: packagingprinting@consultant.com
With almost 27 years of experience in the printing industry, he offers proactive recommendations on anilox roll specifications, flexographic printing sleeves, testing, inventory management, flexographic equipment applications, training, representation from experience in technical sales, marketing, production, technical service, parts, and supplies. His experience covers the spectrum of flexographic markets including wide web flexible packaging, narrow web, tag & labels, foil, folding carton, corrugated packaging applications.


